Related items loading ...
Section 1: Overview
Name of Research Project
Dataset Title
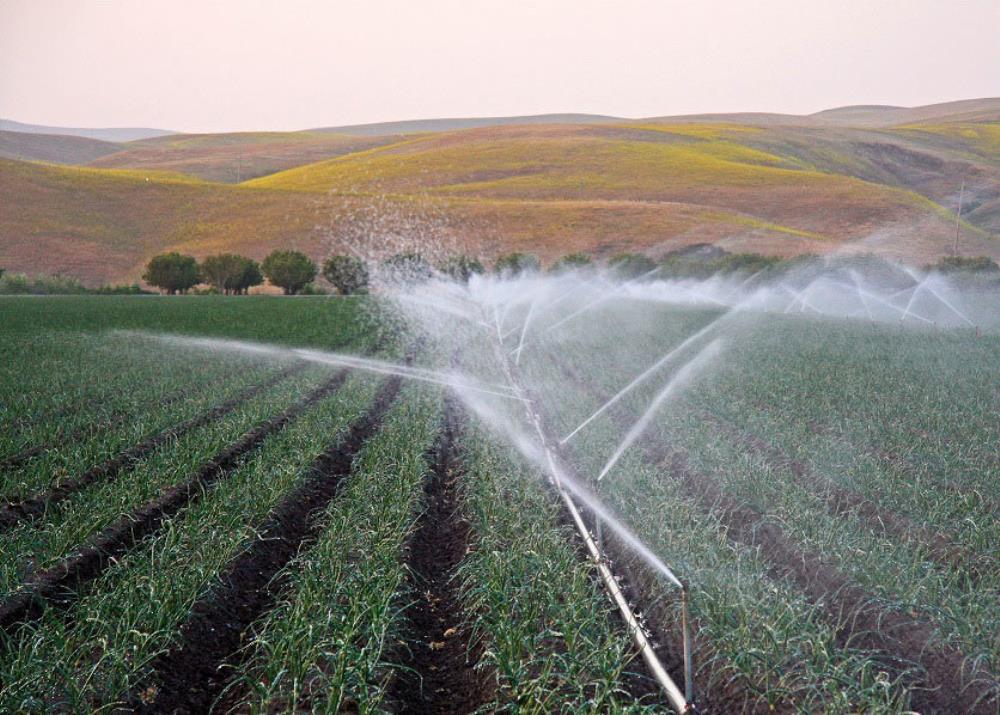
St. Clair - Detroit River System: Total Phosphorus Mass B alance
Creators
|
Scavia, Don | principalInvestigator | | | |
Bocaniov, Serghei | Originator | | | |
Dagnew, Awoke | Collaborator | | | |
Long, Colleen | Collaborator | | | |
Purpose
This data set was developed in order to estimate the total phosphorus budget for the St. Clair – Detroit River system for 1998 through 2016, to support the implementation of the 2012 Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement (GLWQA) on reducing Lake Erie’s phosphorus inputs. This study also identified, for the first time, that loads from resuspended Lake Huron sediment were likely not always detected in US and Canadian monitoring programs, due to mismatches in sampling and resuspension event frequencies, substantially underestimating the load. This additional load increased over time due to climate-induced decreases in Lake Huron ice cover and increases in winter storm frequencies. Given this more complete load inventory, we estimated that to reach a 40% reduction in the Detroit River TP load to Lake Erie, accounting for the missed load, point and non-point sources other than that coming from Lake Huron, and the atmosphere would have to be reduced by at least 50%. Note, this data set was created for a project led by the University of Michigan, and also affiliated with goals of "Lake Futures: Enhancing Adaptive Capacity and Resilience of Lakes and Their Watersheds". Lake Futures is a Pillar 3 project under the Global Water Futures Program funded by Canada First Research Excellence Fund.
Abstract
This study integrated United States and Canadian data to update and extend total phosphorus (TP) loads into and out of the St. Clair-Detroit River System for 1998-2016. The nutrient budgets for Lake St. Clair were calculated for each water year (October 1 to September 30) from 1998 to 2016. Daily flow into and out of the St. Clair River, Lake St. Clair, and the Detroit River were obtained from the US and Canadian river flow gauged stations. The annual TP loads into and out of the river-lake system were estimated from daily flow values and observations of TP concentration using a weighted regressions of time, discharge and season method. The Lake St. Clair annual TP mass balance was used to estimate annual TP retention as the difference between the amount of nutrients entering and leaving the lake.
Keywords
|
Lake |
St. Clair - Detroit River System including Lake Erie (USA-Canada) |
Citations
Scavia, D., Bocaniov, S. A., Dagnew, A., Long, C., & Wang, Y. C. (2019). St. Clair-Detroit River System: Phosphorus Mass Balance and Implications for Lake Erie Load Reduction, Monitoring, and Climate Change. Waterloo, Canada: Canadian Cryospheric Information Network (CCIN). (
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2018.11.008 ).
Section 4: File Locations
Repository (e.g., FRDR, Dataverse, GitHub)
Current File Locations
Section 5: Download Links
Download Links and/or Instructions
Do these data have access restrictions


 GWFNet
GWFNet Master
Master Data
Data Research
Research Map
Map
 Advanced
Advanced Tools
Tools
 . . .
. . .
 Metadata Editor
Metadata Editor
 Record List
Record List
 Alias List Editor
Alias List Editor
 Legacy sites
Legacy sites